Customer-centric product management focuses on solving real customer problems by prioritizing their needs and feedback throughout product development. Here's why it matters:
- Customer retention is cheaper: Retaining a customer costs five times less than acquiring a new one.
- Profitability improves: Companies prioritizing customers are 60% more profitable than those that don't.
- Better product outcomes: Insights from customers reduce the risk of launching features nobody wants.
Key practices include:
- Empathy: Understand customers' emotions, challenges, and goals through interviews and data.
- Data-driven decisions: Use metrics like churn rate, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and feature usage to guide development.
- Iterative development: Continuously refine products based on user feedback.
Customer-centricity ensures products solve real problems, improve user satisfaction, and boost loyalty. Start by engaging directly with your users, mapping their journey, and integrating their feedback into every stage of product development.
Webinar: Customer-Obsessed Product Management by AWS Senior Product Manager
Core Principles of Customer-Centric Product Management
These principles shape the way teams approach their daily work and long-term strategies.
Empathy and Deep Customer Understanding
Empathy goes beyond surface-level observations. It’s about understanding what drives customers - their emotions, challenges, and constraints. This kind of insight often uncovers problems that customers themselves might struggle to articulate, sparking meaningful innovation.
"If you see talking to your customers as a 'necessary evil' or a great way to 'validate your ideas' you're missing the point. The best product people invest in spending time with customers simply to understand." - Chris Petersen, Product Leader
Building empathy means looking past basic demographics. For example, crafting backstory personas can help teams visualize a user’s mindset and daily struggles. Think of a working mom juggling meetings while keeping tabs on her kids - this level of detail informs better decision-making, from big-picture strategies to everyday tasks.
The "Jobs to Be Done" framework offers another lens to understand customers. It focuses on why people "hire" a product - what specific job they need it to accomplish, including the emotional reasons behind their choices. This approach helps teams avoid common cognitive traps like anchoring bias (sticking to outdated assumptions) or confirmation bias (only seeing what aligns with existing beliefs). By understanding these deeper motivations, teams can make smarter, data-backed decisions down the line.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Being customer-centric isn’t just about empathy - it’s about blending qualitative insights with hard data. Analytics show what customers are doing, while interviews and observations explain why they’re doing it.
Take Netflix as an example. The company uses extensive behavioral data to recommend content that viewers actually enjoy, rather than simply promoting sponsored material. Similarly, Salesforce’s "IdeaExchange" allows users to propose and vote on new features, helping the product team prioritize updates that users genuinely want.
Tracking the right metrics is essential. Here are a few to consider:
- Churn Rate: Indicates whether users find enough value to stick around.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer satisfaction and their likelihood to recommend your product.
- Time to Value: Tracks how quickly users experience the benefits of your product.
Data-driven decisions aren’t just effective - they’re cost-efficient. By focusing on actual customer needs, you avoid pouring resources into features no one wants. This approach also sets the stage for ongoing improvements through regular iteration.
Iterative Development and Feedback Integration
Products need to evolve alongside customer expectations and market shifts. Establishing feedback loops throughout the product lifecycle - during design, prototyping, and after launch - ensures you catch issues early and refine continuously.
A great example is Samsung’s 2022 rollout of AI-driven customer support. By analyzing feedback in real time, the company boosted engagement by 19%. This iterative process allowed them to adapt quickly and address customer needs more effectively.
To make iteration a habit, schedule regular, open-ended discovery sessions with users. The goal? Learn, don’t validate. Watching customers interact with your product in their natural environment can reveal pain points you might otherwise miss. Use these observations to make targeted improvements that solve real issues.
Methods for Customer Research
To truly understand your customers, it’s essential to combine qualitative and quantitative research. Qualitative methods, like interviews and surveys, provide direct insights into your customers' thoughts and behaviors. Meanwhile, quantitative approaches, such as analyzing analyst reports, reveal broader market trends and patterns. This research shouldn’t be a one-time effort - it’s something to revisit regularly throughout your product's lifecycle [12, 1].
User Interviews and Surveys
User interviews are a powerful way to uncover the motivations and emotions behind customer decisions. They often reveal issues customers struggle to articulate on their own. To get the most out of these interviews, avoid leading questions. Instead of asking, “Would you use this feature?”, try something like, “When was the last time you had trouble with this task?” This approach encourages customers to share genuine, experience-based feedback.
"To find ideas, find problems. To find problems, talk to people." – Julie Zhou, former VP of Product Design, Facebook
Surveys, on the other hand, help validate assumptions on a larger scale. They can capture key metrics like Net Promoter Score or demographic details. Semi-structured interviews strike a balance between consistency and flexibility, allowing you to explore unexpected insights while maintaining focus. To get a fuller picture, combine these qualitative insights with quantitative survey data.
These findings serve as the foundation for mapping out the customer journey.
Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is a way to visualize the entire experience a user has with your product - from their first interaction to their last. This process highlights moments of friction where users may feel frustrated or confused [7, 2]. The ultimate goal? Pinpoint the "AHA!" moment - when users clearly see the value of your product - and streamline the path to get them there faster.
When creating a journey map, document where pain points arise, how severe the frustrations are, and what workarounds users currently rely on. These insights directly inform product improvements and strategy, helping you address customer frustrations head-on.
Behavioral and Data Analysis
Sometimes, what customers say doesn’t match what they do. That’s where behavioral analysis comes in. By studying how users actually interact with your product, you can uncover patterns that feedback alone might miss. For example, Stitch Fix combines AI algorithms with human stylists to analyze data from style quizzes and customer feedback. This approach has helped them personalize experiences and grow their customer base to over 4 million.
Metrics like churn rate, time to value, and feature usage are invaluable for spotting potential issues. For instance, if you notice a spike in traffic to support articles about a new feature, it could signal user confusion - even if overall usage looks stable. Considering that retaining a customer is five times cheaper than acquiring a new one - and that tech companies typically lose around 10% of users annually - these insights have a direct impact on your bottom line.
Segment your data carefully. Focus on feedback from your most valuable customers rather than reacting to every loud voice. This ensures your efforts are directed where they matter most.
How to Implement Customer-Centric Practices in Product Development
Putting customers at the center of product development starts with addressing internal biases. Recognizing these biases opens the door to a clearer understanding of what your customers truly need. Once that foundation is set, you can take actionable steps to align your product with customer expectations.
Identifying and Prioritizing Customer Needs
To get started, develop detailed personas that reflect your customers' daily lives and challenges. Think about their routines - what frustrates them first thing in the morning, what tools they rely on to solve problems, and where they encounter obstacles.
Go a step further by observing customers in their natural environment. This can reveal subtle yet critical friction points they might not articulate themselves. Before diving into full-scale development, validate your prototypes with real users to ensure you're solving the right problems.
When deciding which features to prioritize, structured frameworks can help guide the process:
Method | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
MoSCoW | Divides features into Must have, Should have, Could have, and Will not have | Identifying essential versus optional requirements |
RICE | Scores features based on Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort | Making resource allocation decisions with data |
Kano | Categorizes features as Basic, Performance, or Excitement | Balancing functional needs with features that delight users |
For a real-world example, look at Salesforce's "IdeaExchange" forum. Customers submit and vote on feature ideas, and the product team uses these votes to prioritize development based on what users care about most.
"Customers don't know what they want until you show it to them." – Steve Jobs
This approach makes sense when you consider that over 70% of customers in the U.S. say their experience with a product directly influences whether they recommend it to others.
Cross-Functional Team Collaboration
Product development can't thrive in isolation. Every team - whether it's engineering, UX, sales, or customer success - brings unique insights from their interactions with customers. Aligning these teams around a shared source of customer data ensures everyone is working to address the same pain points.
"User experience is the heart of product design. If users struggle, the product fails. Being customer-centric is really as simple as being kind and gaining empathy for your customer, understanding their entire context before, during, and after they use your product." – Prashanthi Ravanavarapu, Product Executive, PayPal
Customer success and support teams, in particular, are treasure troves of firsthand feedback. They hear about recurring issues that traditional research might not catch. Regular cross-team reviews of these insights can help integrate customer perspectives into every workflow. Similarly, sales teams can share why potential customers choose - or reject - your product, helping you avoid building features that don't meet market demand.
Establishing Feedback Loops
Once your priorities and team alignment are in place, the next step is setting up continuous feedback loops. These systems capture customer input across your product's entire lifecycle. A well-structured feedback loop typically involves three stages: collecting and storing feedback, analyzing trends and anomalies, and making decisions based on that data.
Feedback should inform both the "problem space" (defining the issue) and the "solution space" (validating your prototype). During customer interviews, the "Five Whys" technique can help you dig deeper into surface-level complaints to uncover the root causes. After gathering qualitative feedback, use tools like affinity diagrams to visually organize recurring themes, making it easier for cross-functional teams to spot patterns.
"I think one of the unsung heroes of doing feedback loops is that you uncover unknowns early in the process." – Brian Pohuski, Senior Product Manager, UserTesting
Post-launch, your feedback systems should stay active to track inflection points - moments when your product needs to adapt to changing customer expectations. Key metrics like Net Promoter Score, churn rate, and time to value (how quickly users see benefits from your product) can show whether your feedback loops are effective. Considering that retaining customers costs five times less than acquiring new ones, and tech companies lose about 10% of users annually, these systems can have a direct impact on your bottom line.
One way to keep feedback flowing is by creating a community forum where users can suggest, discuss, and vote on features. This not only gives you valuable ideas but also strengthens your relationship with your customers.
Benefits of Customer-Centric Product Management
Focusing on customers leads to better product-market alignment, stronger loyalty, and fewer costly mistakes. By applying the principles and research methods outlined earlier, businesses can achieve these results and understand why prioritizing customer needs is so impactful.
Better Product-Market Fit
When you design products around real customer problems instead of internal assumptions, you’re creating solutions people genuinely need. Validating ideas with real-world feedback ensures you’re not wasting time on features no one wants. This method helps you develop products that are not only desirable but also feasible and practical from the start - rather than just technically impressive.
Increased Customer Loyalty and Revenue Growth
Exceeding customer expectations turns users into advocates. In fact, over 70% of U.S. customers say their experiences influence whether they recommend a product to others. This creates a powerful word-of-mouth effect, which is essentially free marketing.
The financial stakes are high: on average, tech companies lose about 10% of their user base annually, making retention a top priority.
"Client-centric companies are 60% more profitable compared to companies not focused on the customer." – Deloitte
When customers feel their voices are heard - through advisory boards, feedback sessions, or direct collaboration - they’re more likely to trust your brand. This trust translates into higher renewal rates and more predictable revenue streams.
Lower Risk of Product Failure
Customer-centricity helps catch potential issues early through prototype testing and ongoing feedback. This approach allows you to avoid spending months on features that ultimately fail. Instead, you can focus your resources on what customers truly value, cutting down on development and maintenance costs. By validating your ideas upfront, you reduce the risk of launching products that fall flat, paving the way for more confident and successful launches.
Customer-Centric vs. Traditional Product Management
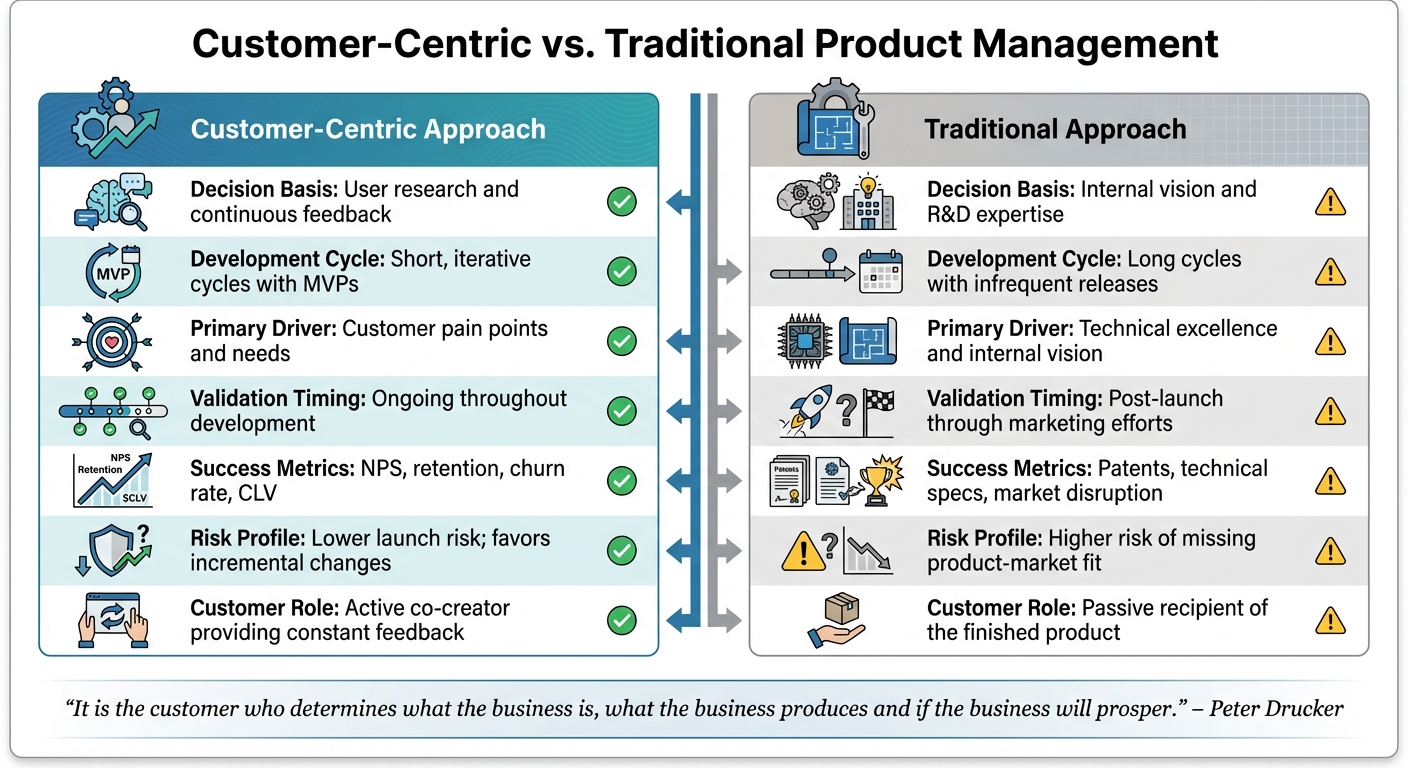
Continuing from our discussion on customer-centric methods, let’s delve into how they stack up against more traditional product management approaches.
The key distinction lies in who influences decisions. Traditional product management often relies on internal R&D and engineering teams, making decisions based on assumptions or technical expertise. On the other hand, customer-centric management prioritizes insights drawn from user research, interviews, and behavioral data, ensuring that customer needs actively shape the product.
This difference reshapes how products are developed. Traditional methods typically follow long development cycles, culminating in major releases. In contrast, customer-centric teams work in shorter cycles, using Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) to test and refine ideas quickly. While traditional methods carry a higher risk of missing product-market fit, customer-centric approaches aim to mitigate these risks by continuously validating ideas. However, this focus on incremental improvements can sometimes overshadow opportunities for bold, groundbreaking innovations.
Even the way success is measured varies significantly. Traditional approaches often celebrate achievements like patents, advanced technical specifications, or market disruption. Meanwhile, customer-centric strategies focus on metrics that directly reflect user satisfaction and business health, such as Net Promoter Score (NPS), retention rates, churn rates, and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
"It is the customer who determines what the business is, what the business produces and if the business will prosper." – Peter Drucker
This ongoing feedback loop inherent in customer-centric methods contrasts sharply with the post-launch evaluation typical of traditional approaches.
Comparison Table
Here’s a side-by-side look at the differences:
Aspect | Customer-Centric Approach | Traditional Approach |
|---|---|---|
Decision Basis | User research and continuous feedback | Internal vision and R&D expertise |
Development Cycle | Short, iterative cycles with MVPs | Long cycles with infrequent releases |
Primary Driver | Customer pain points and needs | Technical excellence and internal vision |
Validation Timing | Ongoing throughout development | Post-launch through marketing efforts |
Success Metrics | NPS, retention, churn rate, CLV | Patents, technical specs, market disruption |
Risk Profile | Lower launch risk; favors incremental changes | Higher risk of missing product-market fit |
Customer Role | Active co-creator providing constant feedback | Passive recipient of the finished product |
Companies like Amazon and Netflix often combine these approaches. They use customer-centric methods to refine user experiences while still leveraging traditional, product-focused strategies in areas like technology development or infrastructure. This balance allows them to innovate while staying closely aligned with customer expectations.
Conclusion
Customer-centric product management is a game-changer when it comes to building products that truly resonate with users. By focusing on customer needs at every step, product teams can minimize the risk of launching features that fall flat, boost retention rates, and carve out a lasting edge in competitive markets.
Consider this: companies that prioritize their customers are 60% more profitable and retain customers at five times lower costs. Plus, over 70% of U.S. customers base their recommendations on product experience.
"User experience is the heart of product design. If users struggle, the product fails. Being customer-centric is really as simple as being kind and gaining empathy for your customer, understanding their entire context before, during, and after they use your product."
– Prashanthi Ravanavarapu, Product Executive, PayPal
The takeaway? A customer-first mindset isn't just a buzzword - it's a continuous effort. Success lies in creating feedback loops, encouraging collaboration across teams, and iterating based on real-world user data. Whether you're conducting user interviews, mapping out customer journeys, or analyzing behavioral trends, each piece of feedback brings you closer to building products that solve real problems.
Start small: shadow a support call, chat with users, or map out a key customer journey. These simple actions can uncover insights that turn good products into great ones. And don’t go it alone - tap into expert communities like the Product Management Society, where you’ll find resources and peers to help you refine your customer-centric skills and tackle modern product challenges.
FAQs
Why is empathy important in customer-centric product management?
Empathy plays a crucial role in customer-focused product management. It goes beyond observing customer behavior - it's about deeply understanding their emotions, needs, and challenges. This connection enables product teams to focus on features that address real issues and craft messaging that speaks to users on a personal level.
Cultivating empathy starts with building emotional awareness. This means asking thoughtful questions, actively listening without judgment, and turning feedback into practical solutions. When product managers hone this skill, they can create products that truly enhance customers' lives and experiences.
What are the key metrics for making data-driven decisions in product management?
Data-driven product management thrives on metrics that turn customer behavior into meaningful insights. Let’s break it down:
- Adoption metrics: These track how well users embrace new features. Think of metrics like feature usage rates or onboarding completion percentages - they show if what you’re building genuinely adds value.
- Engagement metrics: Want to know how engaged users are? Look at session frequency and average session duration. These numbers shed light on how often and deeply users are interacting with your product.
- Retention metrics: These are all about keeping users around. Metrics like churn rates, repeat purchases, or the DAU/MAU ratio give you a clear picture of your product’s stickiness and long-term user loyalty.
On the revenue side, metrics like conversion rates and average revenue per user (ARPU) help product managers zero in on features that not only improve user satisfaction but also drive growth. Pairing these numbers with a customer-first approach - like gathering feedback, analyzing user segments, or mapping out key user journeys - ensures your focus stays on what truly matters to your audience.
For those looking to refine their approach, the Product Management Society provides valuable tools and insights. They’re all about helping product managers turn raw data into strategic decisions that lead to products users genuinely love.
How can companies create effective feedback loops in product development?
To create feedback loops that work, companies need to weave customer input into every phase of the product lifecycle. Start by pinpointing critical moments to collect feedback - this could be through usability testing, in-app surveys, or analyzing user behavior. Make sure a cross-functional team, including product, design, and engineering, takes ownership of this process. Tools like shared backlogs or feedback boards can help organize and prioritize what you learn.
Keep things flexible by building feedback into regular workflows like sprint planning or roadmap updates. For faster results, consider running short "feedback sprints" to test ideas, gather insights, and make changes in just a few days. And don’t forget to close the loop with customers - let them know how their suggestions shaped your decisions. This kind of transparency builds trust and keeps users engaged.
For more tips, product managers can tap into resources, join workshops, or network with peers through the Product Management Society to sharpen their skills in feedback-driven development.
If you’re finding this blog valuable, consider sharing it with friends, or subscribing if you aren’t already. Also, consider coming to one of our Meetups and following us on LinkedIn ✨ And check out our official website.
Connect with the founder on LinkedIn. 🚀





